
This is a small guide on How to fix “not starting portmapper is not running … (warning)” in Debian or Kali Linux.
Fixing “not starting portmapper is not running … (warning)”:
In most Kali or Debian installation users see this warning while booting their system. There’s two ways to fix this, it is up to the readers which one they choose.Solution 1: Disable nfs-common service from startup using chkconfig
If you look intorpcbind script, it says that it
replaces portmapper service. In my mind, there must be some dependencies
somewhere that causes this warning message to appear.The main two services used by
rpcbind are as follows:- NFS (Network File System or
nfs-common) - NIS (Network Information service)
### BEGIN INIT INFO # Provides: rpcbind # Required-Start: $network $local_fs # Required-Stop: $network $local_fs # Default-Start: S 2 3 4 5 # Default-Stop: 0 1 6 # Short-Description: RPC portmapper replacement # Description: rpcbind is a server that converts RPC (Remote # Procedure Call) program numbers into DARPA # protocol port numbers. It must be running in # order to make RPC calls. Services that use # RPC include NFS and NIS.Of these two it seems
nfs-common causes the most issues, so we are just going to disable that.If you don’t use NFS functionality right now then you can disable NFS at startup.
First of all install
chkconfig application.apt-get install chkconfig -yNow use the following command to list
nfs-common service, it’s runlevel and dependencies.chkconfig -l nfs-common --depsAs you can see from the screenshot below, it’s dependencies are
$portmap and $time.Note: Use
chkconfig -l servicename --deps to find out dependencies for any services. This is particularly useful when you have vague idea on what you’re after.If you are happy with the findings and want to remove it from startup, issue the following command
chkconfig --del nfs-commonFrom the output, your can see
nfs-common is now disabled from run-levels.In case you’ve found that this is causing more trouble than actually fixing, (i.e.
nfs-common
being used by another service and now you’re getting errors), you can
revert your change back easily. To revert your changes back, use the
following command:chkconfig --add nfs-commonAgain, from the screenshot below, you can see
nfs-common is back in startup with exactly the same run levels as before.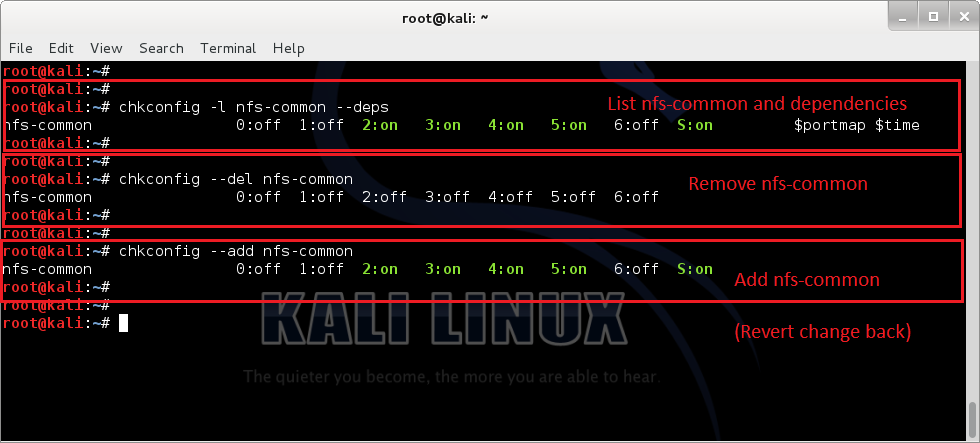
Then reboot. Next time you shouldn’t see that warning anymore.
A similar problem with Pulse Audio If you also have pulseaudio warning during boot time, If you have pulseaudio warning during Kali or Debian Linux during boot up then follow this guide Fixing PulseAudio configured for per-user sessions … (warning) in Kali Linux and Debian.
Solution 2: Enabling rpcbind defaults
I was notified that this is not the best solution and it enables unnecessary services to load at startup and makes your system vulnerable. However, if you’re not too worried about that, then go ahead …update-rc.d rpcbind defaults update-rc.d rpcbind enable
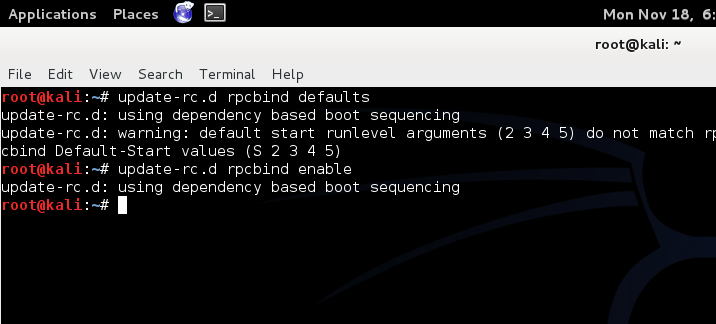
That’s it, Next time you shouldn’t see that warning anymore.
If you also have pulseaudio warning during boot time, Fixing PulseAudio configured for per-user sessions … (warning) in Kali Linux and Debian.
Portmap
The portmapper (rpc.portmap or just portmap, or rpcbind) is an Open Network Computing Remote Procedure Call (ONC RPC) service that runs on network nodes that provide other ONC RPC services.Version 2 of the port mapper protocol maps ONC RPC program number/version number pairs to the network port number for that version of that program. When an ONC RPC server is started, it will tell the port mapper, for each particular program number/version number pair it supports for a particular transport protocol (TCP or UDP), what port number it is using for that particular program number/version number pair on that transport protocol. Clients wishing to make an ONC RPC call to a particular version of a particular ONC RPC service must first contact the port mapper on the server machine to determine the actual TCP or UDP port to use.
Versions 3 and 4 of the protocol, called the rpcbind protocol, map a program number/version number pair, and an indicator that specifies a transport protocol, to a transport-layer endpoint address for that program number/version number pair on that transport protocol.
The port mapper service always uses TCP or UDP port 111; a fixed port is required for it, as a client would not be able to get the port number for the port mapper service from the port mapper itself.
The port mapper must be started before any other RPC servers are started.
Example portmap instance
This shows the different programs and their versions, and which ports they use. For example, it shows that NFS is running, both version 2 and 3, and can be reached at TCP port 2049 or UDP port 2049, depending on what transport protocol the client wants to use, and that the mount protocol, both version 1 and 2, is running, and can be reached at UDP port 644 or TCP port 645, depending on what transport protocol the client wants to use.$ rpcinfo -p program vers proto port 100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper 100000 2 udp 111 portmapper 100003 2 udp 2049 nfs 100003 3 udp 2049 nfs 100003 4 udp 2049 nfs 100003 2 tcp 2049 nfs 100003 3 tcp 2049 nfs 100003 4 tcp 2049 nfs 100024 1 udp 32770 status 100021 1 udp 32770 nlockmgr 100021 3 udp 32770 nlockmgr 100021 4 udp 32770 nlockmgr 100024 1 tcp 32769 status 100021 1 tcp 32769 nlockmgr 100021 3 tcp 32769 nlockmgr 100021 4 tcp 32769 nlockmgr 100005 1 udp 644 mountd 100005 1 tcp 645 mountd 100005 2 udp 644 mountd 100005 2 tcp 645 mountd 100005 3 udp 644 mountd 100005 3 tcp 645 mountd
Thanks for reading.
Note: This surely fixed my problem (I don’t use NFS), however, I am interested to know if this fixed your problem as well. Let me know, leave a comment. Thanks.
Post a Comment